Conveyor Shaft Guide for Industrial Systems
In many conveyor systems, performance issues such as vibration, uneven movement, excessive noise, or premature bearing failure often originate from one overlooked component: the conveyor shaft. When a shaft is poorly designed or incorrectly selected, it can reduce system efficiency, increase maintenance costs, and cause unplanned downtime. Engineers and maintenance teams need a clear understanding of how conveyor shafts function, how to select the right type, and how to prevent common failures.
This guide provides practical, engineering-focused insights to help you choose and maintain the right conveyor shaft for reliable, long-term conveyor operation.
What Is a Conveyor Shaft?
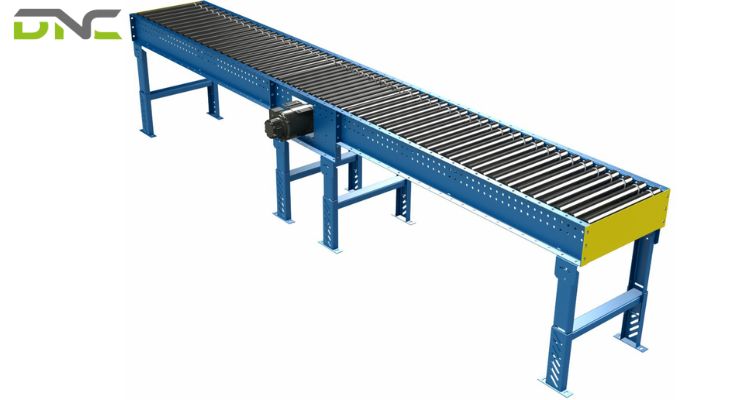
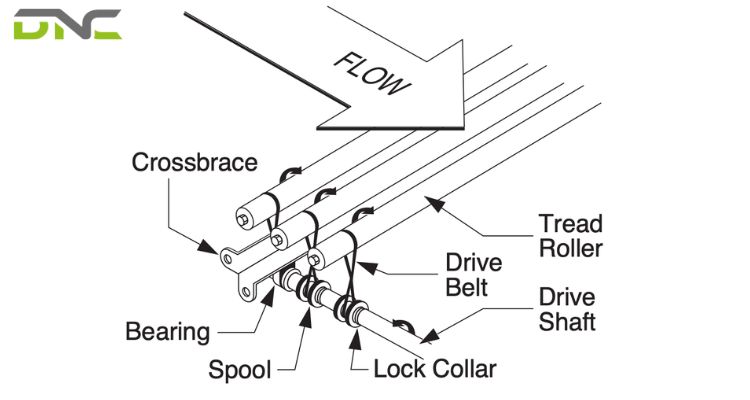
A conveyor shaft is a mechanical component that transmits rotational force within a conveyor system, typically connecting rollers, pulleys, sprockets, or drive units. It supports loads, maintains alignment, and ensures smooth torque transfer throughout the conveyor line. Conveyor shafts are commonly found in roller conveyors, belt conveyors, chain conveyors, and powered conveyor systems.
Depending on the application, shafts may be solid or hollow and manufactured from different steel grades to handle varying loads, speeds, and environmental conditions. Proper shaft selection directly affects conveyor reliability, efficiency, and service life.
Types of Conveyor Shafts
Understanding the different types of conveyor shafts helps engineers select the most suitable option for specific operating conditions. A conveyor shaft may look simple, but its design varies significantly depending on load requirements, drive configuration, and conveyor type.
- Solid Conveyor Shafts: Solid shafts are widely used in heavy-duty conveyor systems where high torque transmission and load capacity are required. Their solid construction offers excellent resistance to bending and torsional stress, making them ideal for long conveyor runs or high-load applications.
- Hollow Conveyor Shafts: Hollow shafts reduce overall weight while maintaining sufficient strength. They are often used in applications where energy efficiency and reduced rotational inertia are important, such as high-speed or long-distance conveyors.
- Keyed Conveyor Shafts: Keyed shafts include a machined keyway that allows secure torque transmission between the shaft and mounted components. They are commonly used in driven rollers, sprockets, and pulleys where slippage must be avoided.
- Threaded Conveyor Shafts: Threaded shafts are designed for easy assembly and disassembly. They are often used in light to medium-duty conveyors where maintenance accessibility is a priority.
Materials Used in Conveyor Shafts
Material selection plays a critical role in shaft durability, wear resistance, and performance under load
- Carbon Steel Conveyor Shafts: Carbon steel shafts offer a strong balance between cost and mechanical strength. They are suitable for most general industrial conveyor systems and provide good machinability and load resistance.
- Stainless Steel Conveyor Shafts: Stainless steel shafts are ideal for corrosive or hygienic environments. They resist rust, chemical exposure, and moisture, making them suitable for food processing, pharmaceutical, and cleanroom conveyor systems.
- Hardened or Heat-Treated Shafts: Heat-treated shafts provide increased surface hardness and wear resistance. They are commonly used in high-friction or continuous-duty conveyors where long service life is critical.
Key Design Factors for Conveyor Shafts
Proper shaft design ensures stable operation and prevents premature mechanical failure. Several engineering factors must be evaluated during the design and selection process.
- Load Capacity: The shaft must support both static and dynamic loads without excessive deflection. Incorrect load calculations can lead to bending, misalignment, and bearing damage.
- Torque Transmission: Shaft diameter and material strength must match the required torque output. Under-designed shafts may twist or fail under peak loads.
- Shaft Length and Deflection: Longer shafts are more prone to bending. Engineers must consider allowable deflection limits to maintain roller alignment and smooth conveyor motion.
- Operating Speed: High-speed conveyors require precise shaft balancing to minimize vibration and noise, improving system efficiency and bearing life.
Common Conveyor Shaft Problems and Solutions
Conveyor shaft issues often develop gradually and can be prevented with proper design and maintenance. Identifying early warning signs helps reduce downtime and repair costs.
- Shaft Misalignment: Misalignment increases bearing wear and causes uneven roller movement. Regular alignment checks and precision machining help prevent this issue.
- Shaft Wear and Fatigue: Continuous operation under heavy loads can cause surface wear or fatigue cracks. Using hardened materials and proper lubrication extends shaft lifespan.
- Excessive Vibration: Vibration often results from poor balancing or incorrect shaft diameter. Dynamic balancing and correct sizing improve conveyor stability.
Conveyor Shaft Applications Across Conveyor Systems
Conveyor shafts are used across a wide range of industrial conveyor designs.Their function and configuration vary depending on system requirements.
- Roller Conveyors: Shafts support and rotate rollers, ensuring smooth product movement and load distribution.
- Belt Conveyors: In belt conveyors, shafts are used in drive pulleys and idlers to transmit power and maintain belt tension.
- Chain Conveyors: Shafts connect sprockets and drive components, handling high torque and heavy loads in demanding environments.
Conveyor Shaft Comparison by Design Type
The table below compares common conveyor shaft designs based on performance and application
| Comparison Criteria | Solid Shaft | Hollow Shaft | Keyed Shaft |
|---|---|---|---|
| Load Capacity | High | Medium | Medium to High |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight | Medium |
| Torque Transmission | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Maintenance Ease | Moderate | Moderate | Easy component locking |
| Typical Applications | Heavy-duty conveyors | High-speed conveyors | Driven rollers and pulleys |
How to Select the Right Conveyor Shaft
Selecting the correct conveyor shaft requires balancing performance, durability, and cost.
A structured evaluation process ensures long-term system reliability.
- Assess Operating Conditions: Consider load weight, operating hours, speed, and environmental exposure before choosing shaft material and design.
- Match Shaft Design to Conveyor Type: Different conveyor systems impose unique mechanical demands. Shaft selection must align with system configuration and drive method.
- Plan for Maintenance and Replacement: Choosing standardized or custom shafts with accessible mounting simplifies future maintenance and reduces downtime.
Why Is DNC Automation a Trusted Partner for Conveyor Shaft Solutions?
DNC Automation is a trusted partner for conveyor shaft design, selection, and integration in modern automation systems. With strong engineering expertise and practical industry experience, DNC Automation delivers conveyor shaft solutions that align with real operational demands, ensuring durability, precision, and long-term performance across diverse conveyor applications.
Choosing the right conveyor shaft can significantly improve efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, and extend system lifespan. Contact DNC Automation now to discuss your conveyor requirements and receive expert guidance tailored to your automation needs.
- 0 views
- 0 Comment





Recent Comments