Warehouse Management System (WMS) – The Foundation of Smart Warehouse Operations
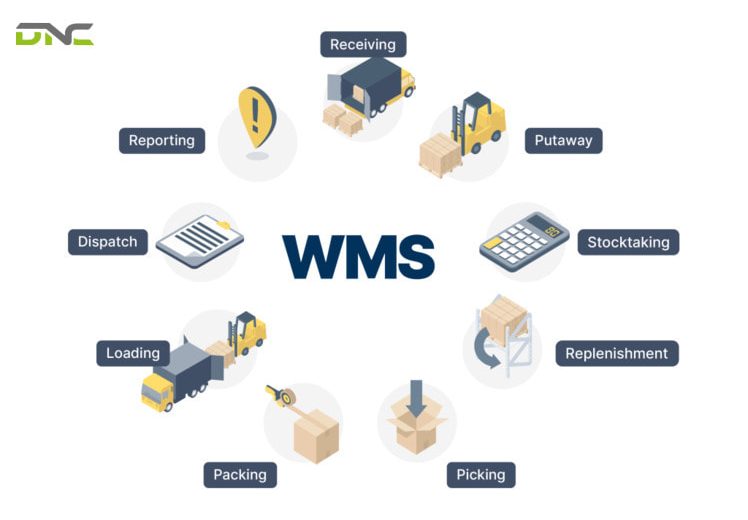
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) have evolved from optional software to essential infrastructure. WMS serves as the digital foundation orchestrating all warehouse activities—from receiving and storage through picking and shipping—while providing the data visibility and process control necessary for modern smart warehouse operations aligned with Industry 4.0 objectives.
What Exactly Is a Warehouse Management System (WMS)?
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is comprehensive software that manages and optimizes all warehouse operations and material flows. Acting as the central intelligence platform, WMS coordinates receiving activities, determines optimal storage locations, manages inventory accuracy, orchestrates order fulfillment processes, coordinates shipping operations.
For Malaysian operations implementing automation, WCS transforms disconnected equipment into cohesive systems. Without WCS, each conveyor, robot, or sorter operates independently requiring manual coordination.
With WCS, equipment works as integrated networks automatically optimizing throughput, preventing collisions, balancing workloads, and adapting to equipment failures or changing priorities.
How Does a Warehouse Control System Work?
WCS operates through continuous cycles of receiving instructions, optimizing execution plans, directing equipment, monitoring performance, and adapting to real-time conditions.
Step 1: Receiving Data from Business Systems
WMS operations begin with data from upstream systems. ERP systems transmit purchase orders indicating expected inbound shipments. E-commerce platforms send customer orders requiring fulfillment. Retail systems generate store replenishment orders. Manufacturing systems request component deliveries.
This inbound data provides WMS with business context needed to plan and execute warehouse activities. Upon receiving purchase orders, WMS prepares for inbound shipments—allocating dock doors, scheduling labor, pre-planning storage locations.
Step 2: Optimizing Storage Location Allocation
As products arrive, WMS determines optimal storage locations through sophisticated algorithms. Velocity analysis identifies fast-moving items that should occupy prime locations near shipping areas minimizing travel distance.
Slow-movers are directed to denser storage in less accessible areas. Product dimensions, weight, and special requirements (temperature control, hazardous materials, security) influence location selection. The system considers space utilization directing products to locations matching their dimensions efficiently.
Step 3: Directing Workers or Automated Equipment
WMS generates work instructions directing warehouse activities. For manual operations, workers receive tasks on handheld devices—”Travel to Location A-12-03, Pick 5 units of SKU 12345.” The system optimizes task sequences minimizing travel distance and balancing workload across available workers.
Step 4: Real-time Order and Inventory Tracking
Throughout all activities, WMS maintains current visibility. As workers complete picks, scan confirmations update order status immediately—customers see live progress through integrated portals.
As items move between locations, inventory positions update continuously—finance has accurate valuations, purchasing knows exactly what’s available, customer service can promise delivery accurately. WMS tracks worker productivity, identifies bottlenecks, and reveals trends.
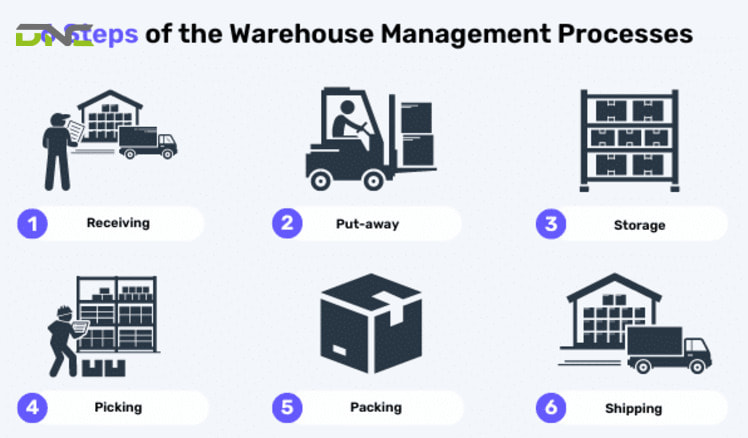
Warehouse Management System (WMS) operates in 4 main steps
What Are the Main Features of a Warehouse Management System?
Modern WMS platforms provide comprehensive functionality supporting all aspects of warehouse operations. Below are the 6 main features of this system:
- Inventory Control and Accuracy: Precise tracking of item location, quantity, status (available, reserved, quarantined), and characteristics (SKU, batch/lot, serial number, expiration date).
- Order and Shipment Management: Manages orders from receipt to delivery, including validation and wave planning. Guides correct packaging and integrates with shipping for label generation, tracking data, and carrier optimization.
- Real-time Data Tracking and Visibility: Provides instant inventory snapshots and mobile accessibility for remote monitoring.Integrates with customer portals for self-service visibility.
- Location and Space Optimization: Uses intelligent slotting algorithms to optimize product placement.
- Integration Capabilities: Connects with various enterprise systems via APIs and standard protocols.
- Analytics and Reporting: Transforms operational data into business intelligence. Provides standard reports on valuation, fulfillment performance, labor, space, and accuracy.
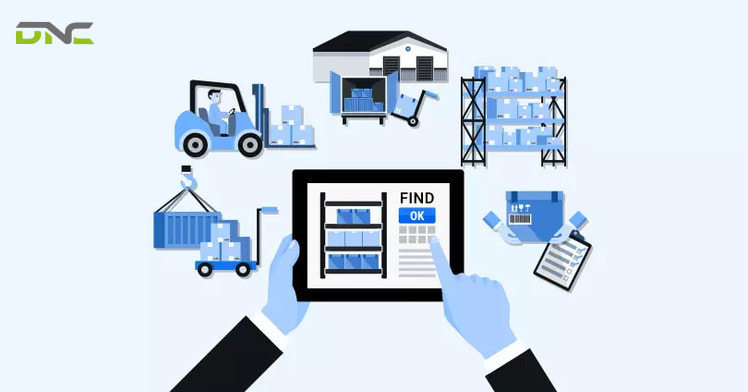
Modern WMS platforms provide comprehensive functionality supporting all aspects of warehouse operations.
What Are the Main Benefits of Using a Warehouse Control System?
A Warehouse Control System (WCS) acts as a critical bridge between the high-level planning of a Warehouse Management System (WMS) and the actual operation of automated material handling equipment (MHE) on the floor. Here are 5 benefits that a WCS system provides:
- Optimized Material Flow: WCS eliminates congestion and bottlenecks through intelligent routing. Systems dynamically balance loads across equipment preventing overutilization while maximizing throughput.
- Increased Operational Efficiency and Reduced Errors: Automated equipment control eliminates manual intervention reducing human errors in equipment operation. Optimized task sequencing minimizes wasted motion and empty travel.
- Enhanced Monitoring and Proactive Maintenance: Real-time equipment monitoring detects performance degradation before failures. Predictive maintenance alerts schedule repairs during planned downtime rather than reacting to unexpected breakdowns.
- Real-time Data Integration and Inventory Accuracy: Automated data capture eliminates manual tracking errors. Every material movement updates inventory systems instantly providing accurate stock visibility.
- Improved ROI on Automation Investments: WCS maximizes returns from expensive automation equipment by optimizing utilization and performance. Equipment operates at designed capacity rather than sitting idle from poor coordination.

5 benefits that a WCS system provides
What’s the Difference Between WMS and WCS?
The relationship between a Warehouse Management System (WMS) and a Warehouse Control System (WCS) is often a source of confusion, as both are critical software components in a modern warehouse. While both aim to optimize operations, they operate at different levels of execution and control.
| Feature | WMS (Warehouse Management System) | WCS (Warehouse Control System) |
| Primary Purpose | Manage inventory, orders, storage strategies | Control and optimize material handling equipment |
| Operational Level | Business logic and planning layer | Equipment execution and control layer |
| Decision Scope | What to move, where to store, how to pick | How equipment moves items, routing paths, timing |
| Time Horizon | Minutes to hours (order waves, replenishment) | Seconds to minutes (real-time equipment control) |
| Key Functions | Receiving, putaway, inventory tracking, order management, shipping | Equipment coordination, traffic management, task optimization, performance monitoring |
| Typical Users | Warehouse managers, inventory planners, supervisors | Operations engineers, maintenance teams, automation specialists |
| Data Focus | Inventory accuracy, order status, labor productivity | Equipment utilization, throughput rates, system performance |
| Example Tasks | Generate pick list for 100 orders | Route totes through conveyors to correct picking stations |
What Challenges Can Occur Without a Proper WCS?
In a fast-moving warehouse environment, even small inefficiencies can have a big impact on overall performance. Without a proper Warehouse Control System (WCS) in place, operations often rely on manual coordination or disconnected automation equipment — leading to delays, errors, and unnecessary costs.
- Poor System Synchronization: Without WCS coordination, automated equipment like conveyors, robots, and sorters operate independently.
- Reduced Productivity and Flow Bottlenecks: Uncoordinated equipment creates congestion points where materials accumulate, while other areas are underutilized.Systems lack the adaptive capacity management needed to handle peak periods, causing operations to be easily overwhelmed.
- Limited Visibility and Reactive Maintenance:Without continuous WCS monitoring, equipment problems are often undetected until a failure occurs. Maintenance becomes reactive rather than proactive, with performance degradation going unnoticed.
- Inability to Scale Operations: A WCS is necessary to ensure that adding capacity does not also proportionally increase operational complexity or labor requirements, making scalable automation impossible without it.

Poor System Synchronization
Frequently Asked Questions About WCS
1. What’s the main difference between WCS and MES?
WCS (Warehouse Control System) focuses specifically on material handling equipment in warehouses and distribution centers—controlling conveyors, sorters, AS/RS, and AGVs. MES (Manufacturing Execution System) manages production processes on factory floors—tracking work orders, machine operations, quality control, and production scheduling.
While both operate at execution levels, WCS handles logistics automation while MES manages manufacturing operations. Some facilities implement both—MES controlling production equipment, WCS managing component supply and finished goods distribution.
2. Can WCS control equipment from different vendors?
Yes, modern WCS platforms support multi-vendor environments through standardized industrial protocols and flexible integration capabilities. Systems communicate with conveyors from one supplier, sorters from another, and robots from a third vendor.
This vendor-neutral approach allows businesses to select best-in-class equipment for each function rather than being locked into single-vendor solutions. DNC’s WCS implementations regularly integrate equipment from 3-5 different manufacturers creating cohesive systems from diverse components.
3. How long does WCS deployment take?
Implementation timelines depend on facility complexity and existing automation: basic WCS for simple conveyor systems deploys in 6-12 weeks, moderate complexity facilities with multiple equipment types require 3-5 months.
4. Is WCS suitable for small or medium-sized warehouses?
Absolutely. While historically associated with large automated facilities, modern cloud-based WCS platforms serve operations of all sizes. Small warehouses with basic conveyor systems benefit from optimization and monitoring capabilities.
The decision depends more on automation level than facility size—any operation with multiple automated equipment types benefits from WCS coordination. Cloud-based subscription models make WCS financially accessible to Malaysian SMEs without massive upfront software investments.
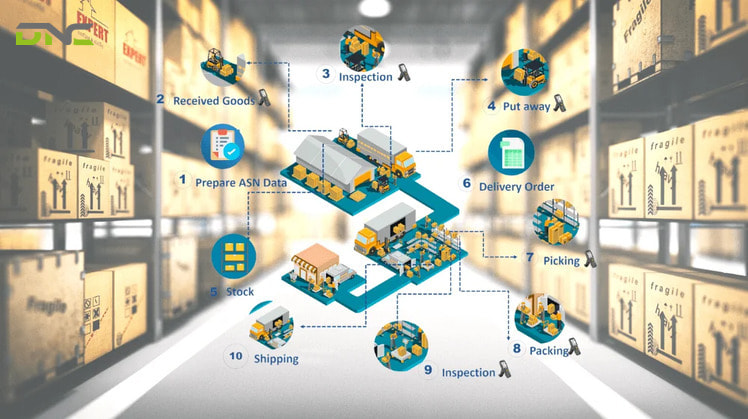
WCS (Warehouse Control System) focuses specifically on material handling equipment in warehouses and distribution centers—controlling conveyors, sorters, AS/RS, and AGVs.
Why Choose DNC Automation for Your Warehouse Control System?
A Warehouse Control System is only as effective as the team that designs and integrates it. At DNC Automation, we combine deep industry expertise with proven automation technology to deliver high-performance, reliable, and scalable WCS solutions tailored to your operation.
- Over 10 years of experience in factory and warehouse automation projects.
- End-to-end integration with conveyors, AS/RS, robotic systems, and WMS.
- Custom-engineered solutions optimized for your layout, capacity, and workflow.
- Proven track record in manufacturing, logistics, and cold chain applications.
- Data-driven control and visibility for improved throughput and accuracy.
- Comprehensive technical support and maintenance services across Malaysia.
- 1 views
- 0 Comment



Recent Comments