Bucket Elevator Conveyor Solutions for Efficient Vertical Material Handling
A bucket elevator conveyor is a reliable solution for vertically transporting bulk materials in industrial production lines. With a compact design, high capacity, and easy integration into automated systems, bucket elevators are widely used in industries such as food processing, cement, chemicals, and mining. This article explains how bucket elevator conveyors work, their key components, advantages, and how to select the right solution for industrial applications.
What Is a Bucket Elevator Conveyor?
A bucket elevator conveyor is a specialized material handling system designed to transport bulk materials vertically using a series of buckets attached to a belt or chain. It is commonly used in industrial environments where materials must be lifted efficiently from a lower elevation to a higher discharge point within a limited footprint.
Unlike horizontal conveyors, bucket elevators are optimized for vertical or near-vertical transport, making them ideal for facilities where floor space is constrained. They are widely integrated into automated production lines due to their high throughput, controlled material flow, and reliability.
Compared to other conveying solutions:
- Belt conveyors are better suited for horizontal or inclined transport.
- Screw conveyors handle short vertical distances but struggle with high lift heights.
- Bucket elevator conveyors excel in long vertical lifts with consistent capacity.
What Types of Materials Can a Bucket Elevator Conveyor Handle?
Bucket elevator conveyors are designed to handle a wide range of bulk materials, depending on system configuration and material characteristics.
Common material types include:
- Granular materials: grains, seeds, pellets, plastic resin
- Powders and fines: cement, flour, chemicals, mineral powders
- Heavy or abrasive materials: sand, clinker, aggregates
- High-temperature materials: hot ash, processed minerals (with proper design)
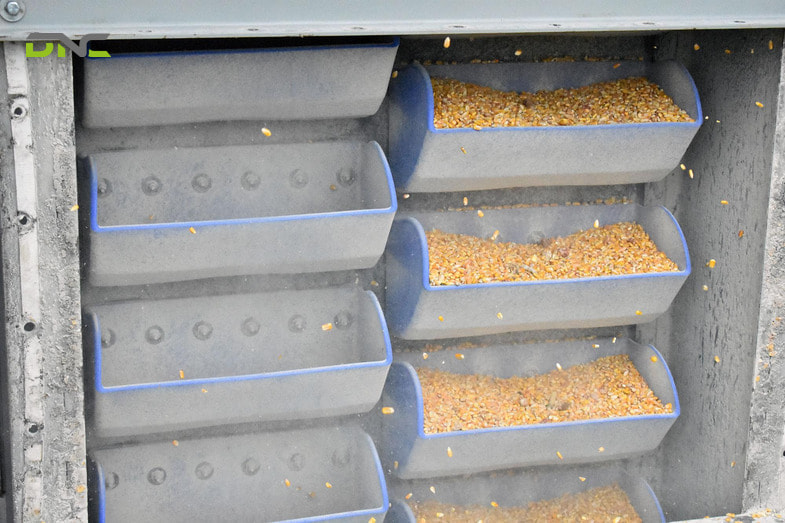
Key material properties that influence system design:
- Bulk density
- Particle size and shape
- Flowability
- Abrasiveness
- Moisture content
Understanding these parameters is critical to selecting the right bucket type, elevator speed, and construction materials.

Key material properties that influence system design
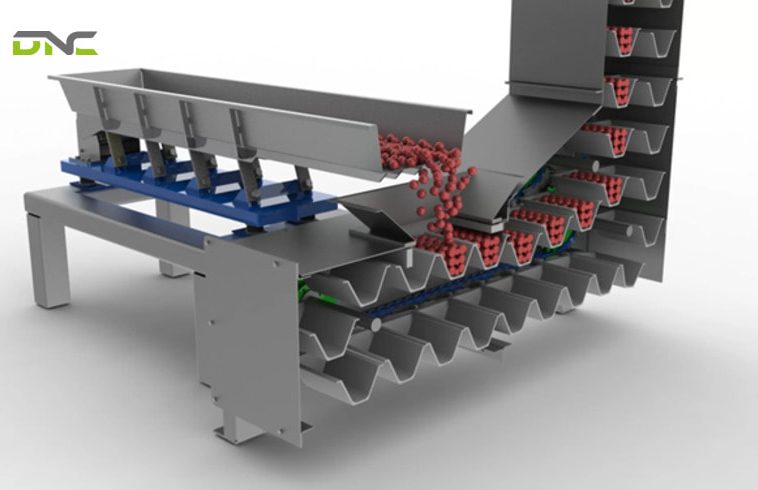
What Are the Main Components of a Bucket Elevator Conveyor System?
A bucket elevator conveyor consists of several integrated components working together as a system:
Buckets
Buckets are the primary material-carrying elements of the elevator. They are mounted at regular intervals along the belt or chain and are responsible for lifting and discharging bulk materials.
Key design considerations include:
- Material: carbon steel for general applications, stainless steel for food or corrosive environments, and plastic for lightweight or hygienic handling
- Shape: Deep buckets for high-capacity, free-flowing materials
- Volume and pitch: directly influence throughput, elevator speed, and material stability
Selecting the correct bucket type is essential to prevent material degradation, spillage, and excessive wear.
Belt or Chain
The belt or chain acts as the traction element that moves the buckets vertically through the elevator casing.
- Lightweight and energy-efficient
- Lower noise levels
- Ideal for clean, dry, and non-abrasive materials
- Commonly used in food, agriculture, and light industrial applications
The choice between belt and chain depends on material characteristics, operating conditions, lift height, and required service life.
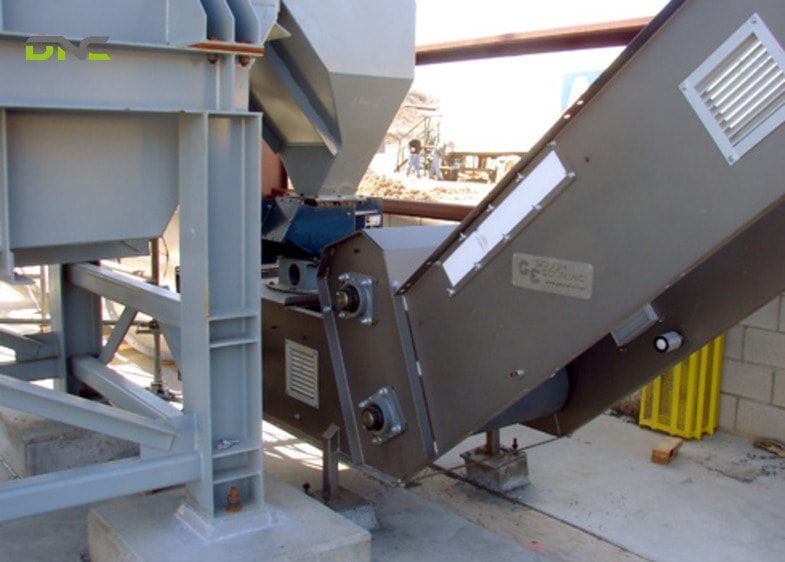
Head Section
The head section is located at the top of the bucket elevator and serves as the discharge and drive area.
Main functions include:
- Housing the drive motor and gearbox
- Supporting the head pulley or sprocket
- Controlling the material discharge process through centrifugal force or gravity
- Directing material into downstream equipment via the discharge chute
A well-designed head section ensures smooth discharge while minimizing material carryback and wear.
Boot Section
The boot section is positioned at the bottom of the elevator and is where material enters the system.
Key features include:
- Material inlet chute designed to regulate feed rate
- Take-up or tensioning device to maintain proper belt or chain tension
- Clean-out doors for maintenance and inspection
Proper boot design prevents overloading, material buildup, and premature component failure.
Casing
The casing is the enclosed structural housing that surrounds the entire elevator.
Its functions include:
- Containing material and preventing spillage
- Minimizing dust emissions and environmental contamination
- Protecting personnel from moving components
- Providing structural stability and alignment
Casing designs may include inspection doors, explosion relief panels, and wear liners depending on application and safety requirements.
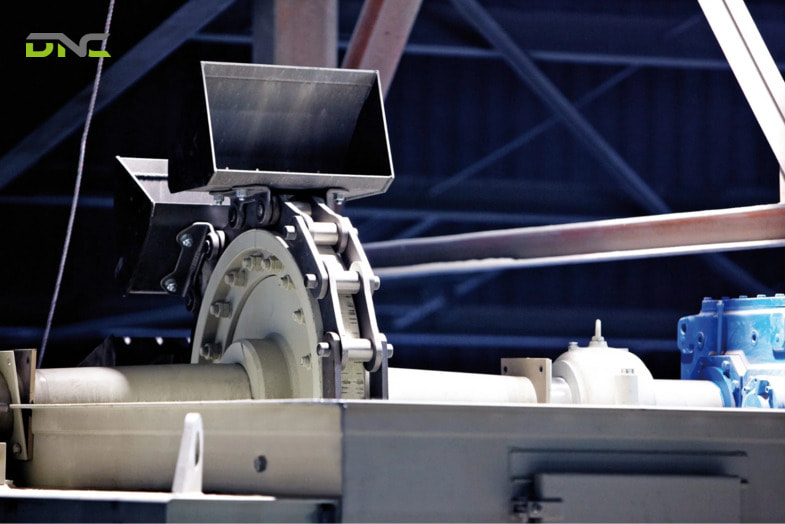
Drive and Safety Systems
Modern bucket elevator conveyor systems are equipped with advanced drive and safety components to ensure reliable and safe operation.
Key elements include:
- Motor and gearbox: sized to handle startup loads and continuous operation
- Backstop devices: prevent reverse rotation during power loss
- Speed sensors: detect belt or chain slippage and abnormal operation
- Belt or chain misalignment switches: protect against tracking issues
- Level sensors at inlet and discharge points: prevent blockages and overflow
When integrated with PLC and control systems, these safety devices enable real-time monitoring, automatic shutdown, and predictive maintenance.

A bucket elevator conveyor consists of several integrated components working together as a system
How Does a Bucket Elevator Conveyor Work in an Automated Production Line?
The operation follows a continuous and controlled process:
- Material enters the boot section through a regulated inlet.
- Buckets scoop or receive material as they pass through the inlet.
- The belt or chain lifts the material vertically.
- At the head section, material is discharged using centrifugal force or gravity.
- Empty buckets return downward to repeat the cycle.
In automated factories, bucket elevators are often integrated with:
- PLC control systems
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) for speed control
- Interlocks with upstream and downstream equipment
This integration ensures synchronized operation, prevents overloading, and reduces unplanned downtime.

The operation follows a continuous and controlled process
What Are the Advantages and Limitations of Bucket Elevator Conveyors?
Bucket elevator conveyors are widely adopted in industrial material handling due to their unique ability to move bulk materials vertically in a controlled and efficient manner. However, like any engineering solution, they offer both strengths and limitations that must be evaluated carefully during system design.
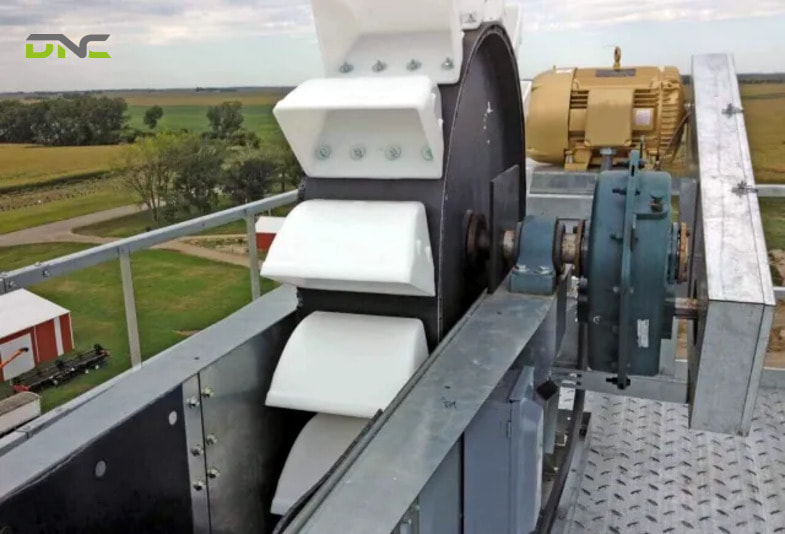
Advantages of Bucket Elevator Conveyors
- Efficient Vertical Material Transport: Bucket elevator conveyors are specifically engineered for vertical or near-vertical lifting. Unlike inclined belt conveyors, which require long horizontal distances, bucket elevators can achieve significant lift heights within a very small footprint.
- Compact Footprint: Because the system is designed to operate vertically, it occupies minimal floor space. This is particularly valuable in production facilities where space is limited or where equipment must be integrated into existing layouts.
- High Throughput Capacity: With properly sized buckets, optimized spacing, and controlled operating speed, bucket elevator conveyors can handle high volumes of material continuously.
- Enclosed Design Minimizes Dust and Spillage: The fully enclosed casing of a bucket elevator conveyor prevents material from spilling into the surrounding environment. This is especially important when handling dusty, fine, or hazardous materials.
- Easy Integration into Automated Systems: Bucket elevator conveyors are well suited for integration into automated material handling systems.
Limitations of Bucket Elevator Conveyors
- Higher Initial Investment Than Simple Conveyors: Compared to basic belt or screw conveyors, bucket elevator systems require more components, heavier structural design, and advanced safety devices.
- Requires Precise Engineering and Alignment: Bucket elevator conveyors demand accurate mechanical design and installation. Incorrect alignment of the belt or chain, improper bucket spacing
- Maintenance Is Critical to Prevent Belt or Chain Failure: Because the system operates continuously under load, routine inspection and maintenance are necessary.

Advantages of Bucket Elevator Conveyors
Which Industries Commonly Use Bucket Elevator Conveyors?
Bucket elevator conveyors are widely used across multiple industries:
- Food & Agriculture: grain handling, flour mills, rice processing
- Cement & Building Materials: clinker, limestone, additives
- Chemical & Fertilizer: powders, granules, compounds
- Mining & Minerals: ore, sand, aggregates
- Animal Feed Production: raw materials and finished feed
Each industry requires different design considerations related to hygiene, abrasion, temperature, and safety standards.
What Technical Factors Should Be Considered When Selecting a Bucket Elevator Conveyor?
Key engineering criteria include:
- Required capacity (tons/hour)
- Vertical lift height
- Material bulk density and behavior
- Environmental conditions (dust, moisture, corrosion)
- Explosion protection (ATEX where applicable)
- Compliance with ISO, CE, or industry-specific standards
A professional system integrator evaluates these factors holistically to avoid undersized or overengineered solutions.
How Does DNC Automation Deliver Bucket Elevator Conveyor Solutions?
DNC Automation provides end-to-end bucket elevator conveyor solutions, not just equipment supply:
- Process analysis and system design
- Custom engineering tailored to material and production requirements
- Fabrication and mechanical installation
- Full automation integration (PLC, HMI, SCADA)
- Commissioning, maintenance, and system upgrades
By focusing on system performance and long-term reliability, DNC Automation helps factories optimize material flow, reduce downtime, and scale production efficiently.
- 9 views
- 0 Comment

Recent Comments