Indexing Conveyor: A Complete Guide for Automated Production Lines
An indexing conveyor is a precision conveyor system designed to move products in controlled steps with accurate positioning at each station. Commonly used in automated assembly, inspection, and packaging lines, indexing conveyors enable synchronized processes, consistent cycle times, and improved product quality. This article explains how indexing conveyors work, their common types, advantages, and key applications in industrial automation.
What Is an Indexing Conveyor?
An indexing conveyor is a type of conveyor system designed to move products in discrete steps rather than continuous motion. The conveyor advances a fixed distance, stops precisely at a defined position (index), allows a process to occur, and then moves again to the next station.
Unlike continuous conveyors that focus on material flow, indexing conveyors are engineered for process accuracy, synchronization, and repeatability. They are commonly used in automated assembly lines, inspection stations, and multi-step manufacturing processes where precise positioning is critical.
Indexing conveyors are a core component in modern automation systems where product quality, cycle time control, and integration with robots or tooling are essential.
How Does an Indexing Conveyor Work?
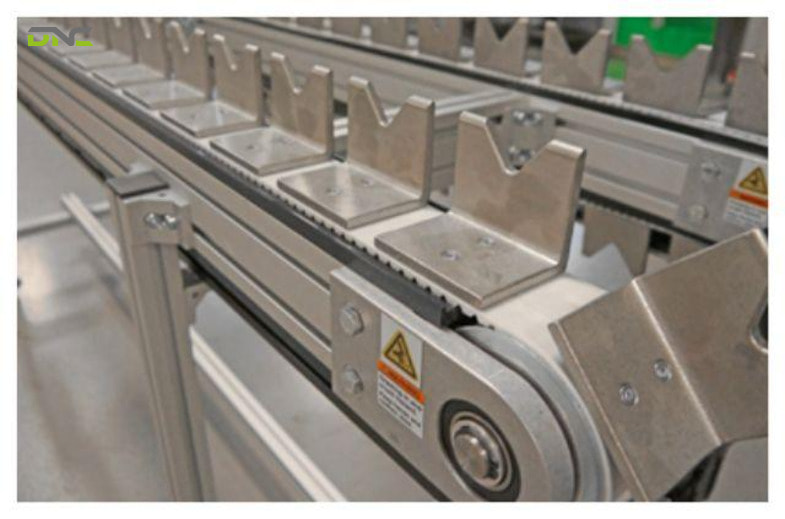
An indexing conveyor operates through a start–stop motion cycle that is tightly controlled by the automation system.
A typical operating sequence includes:
- The conveyor moves a predefined distance.
- The conveyor stops accurately at the work position.
- Processing occurs during the dwell time (assembly, inspection, labeling, etc.).
- Once the operation is complete, the conveyor indexes to the next station.
Key operational concepts:
- Indexing distance: the fixed movement length between stations
- Dwell time: the stop duration required for processing
- Positioning accuracy: ensures repeatable alignment at every station
Servo motors, encoders, and PLCs are typically used to control motion profiles, acceleration, deceleration, and synchronization with other equipment.

How Does an Indexing Conveyor Work?
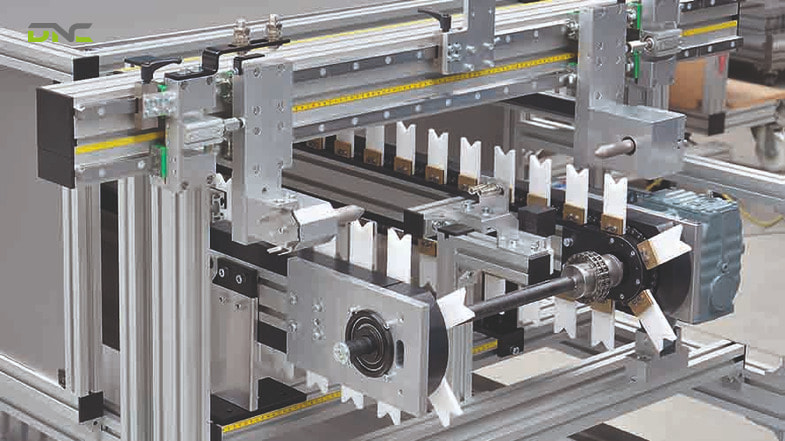
What Are the Main Components of an Indexing Conveyor System?
An indexing conveyor system is composed of mechanical, motion, and control components working together as an integrated unit.
Conveyor Structure and Frame
The rigid frame supports the entire system and maintains alignment. Structural stiffness is critical to ensure positioning accuracy, especially in high-speed or high-load applications.
Drive System
Indexing conveyors commonly use:
- Servo motors for precise positioning
- Gearboxes for torque optimization\
- Mechanical indexing drives in simpler or high-repeat applications
Transport Medium
Depending on the application, the conveyor may use:
- Belts
- Chains
- Pallets with fixtures
Pallet-based systems are especially popular for assembly lines requiring product orientation and stability.
Indexing Mechanism
- Servo-driven indexing for flexible, programmable motion
- Cam-driven or mechanical indexing for fixed, high-speed cycles
Sensors and Control Components
- Photoelectric sensors for product detection
- Encoders for position feedback
- PLCs for logic control
- Safety interlocks and emergency stops

What Are the Main Components of an Indexing Conveyor System?
What Types of Indexing Conveyors Are Commonly Used?
Indexing conveyors can be classified based on mechanical structure, motion principle, and application requirements. Selecting the right type is critical to achieving the desired balance between accuracy, throughput, flexibility, and system cost.
Below are the most commonly used types of indexing conveyor systems in industrial automation.
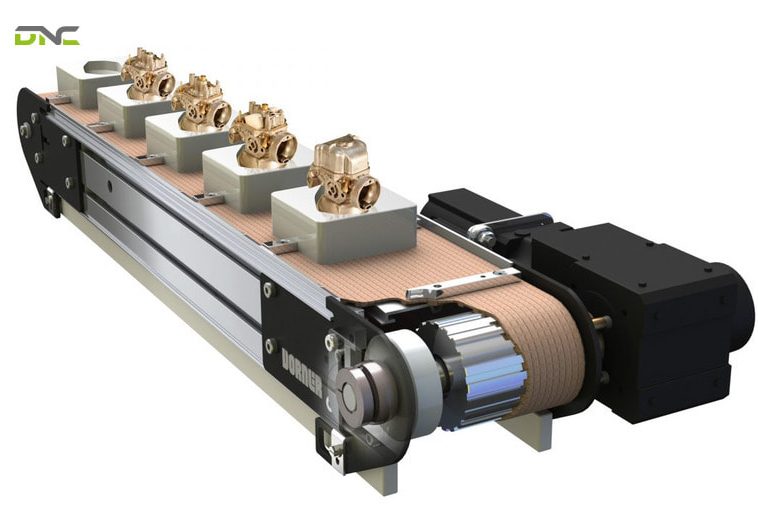
Pallet-Based Indexing Conveyors
Pallet-based indexing conveyors are widely used in automated assembly lines where products must remain stable and precisely positioned throughout multiple processing stations.
In this system, products are mounted on custom pallets or fixtures that travel along the conveyor. Each pallet indexes from one station to the next, ensuring consistent orientation and repeatable positioning.
Key advantages include:
- Excellent positional stability for assembly and inspection
- Easy integration with tooling, robots, and vision systems\
- Ability to handle product variations using interchangeable fixtures
This type is commonly found in automotive components, electronics, and medical device manufacturing.
Belt Indexing Conveyors
Belt indexing conveyors use a belt as the transport medium and move products in controlled step motions rather than continuous flow.
They are best suited for:
- Lightweight products
- Simple indexing applications
- Short to medium conveyor lengths
Belt indexing conveyors offer a cost-effective and low-maintenance solution when extreme positioning accuracy or heavy loads are not required. However, they may require additional guides or fixtures to ensure product stability during indexing stops.
Chain Indexing Conveyors
Chain indexing conveyors are designed for heavy-duty applications where higher loads, harsher environments, or longer conveyor lengths are involved.
Compared to belt systems, chain indexing conveyors provide:
- Higher load capacity
- Greater resistance to impact, abrasion, and contamination
- Improved durability in industrial environments
They are commonly used in automotive, metal processing, and heavy machinery assembly lines, where robust construction and long service life are essential.
Rotary Indexing Tables vs. Linear Indexing Conveyors
Rotary indexing systems move products around a circular table, indexing them between fixed stations arranged radially.
Key characteristics:
- Compact footprint
- High repeatability
- Ideal for applications with a limited number of stations
Rotary indexing tables are often used in high-speed assembly or testing operations with symmetrical layouts.
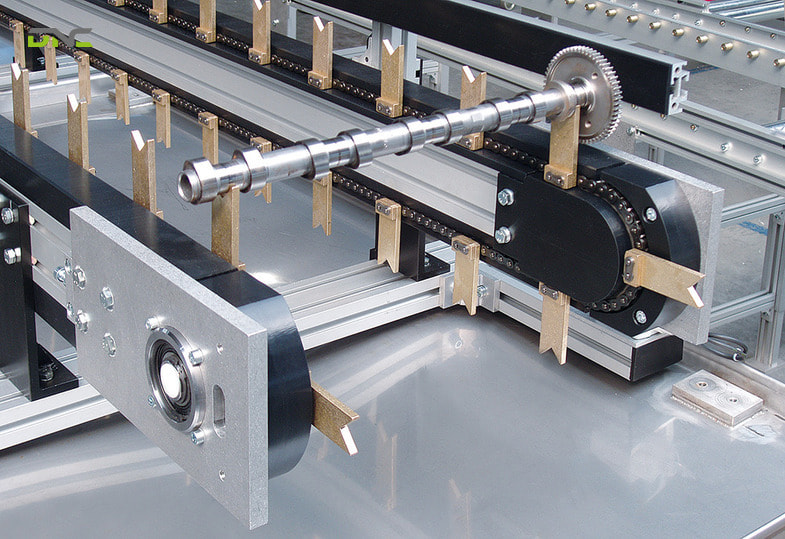
Servo-Driven vs. Mechanical Indexing Systems
Indexing conveyors can be driven by either servo-controlled motion or mechanical indexing mechanisms, depending on flexibility and performance requirements.
Servo-Driven Indexing Systems
- Fully programmable indexing distances and dwell times
- High positioning accuracy and smooth motion profiles
- Easy integration with PLCs, robots, and vision systems
- Ideal for multi-product or frequently changing production lines
Indexing conveyors can be classified based on mechanical structure, motion principle, and application requirements
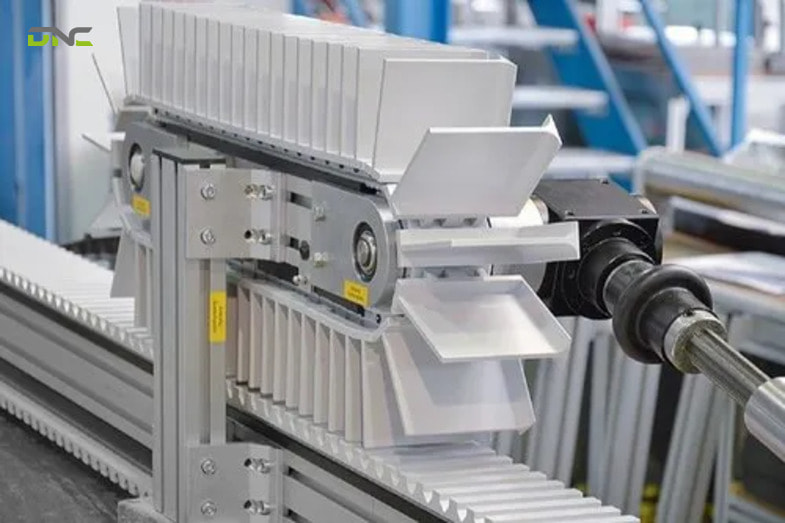
What Are the Advantages and Limitations of Indexing Conveyors?
Indexing conveyors are designed to support manufacturing processes that demand precision, synchronization, and repeatability. While they offer significant performance benefits in automated production lines, they also introduce certain design and cost considerations that must be carefully evaluated.
Advantages of Indexing Conveyors
- High Positioning Accuracy and Repeatability: Indexing conveyors are engineered to move products to exact, repeatable positions at each station. By using servo motors, encoders, and precise motion control, the system ensures that every product stops at the same location during each cycle.
- Process Synchronization Across Multiple Stations: One of the key strengths of indexing conveyors is their ability to synchronize multiple processing stations. All operations occur during the dwell time while the conveyor is stationary, allowing each station to work in parallel.
- Improved Product Quality and Process Consistency: Controlled dwell time ensures that each process step has sufficient time to be completed correctly. This reduces variability between products, minimizes defects, and lowers rework rates.
Limitations of Indexing Conveyors
- Higher System Complexity: Indexing conveyor systems rely on advanced motion control, sensors, and automation logic. This increases the overall system complexity compared to continuous conveyors.
- Higher Initial Investment: Due to the use of precision components such as servo drives, robust mechanical structures, and integrated control systems, indexing conveyors generally involve a higher upfront investment.
- Lower Flexibility If Poorly Designed: If an indexing conveyor is designed solely around a single product or fixed process, adapting it to new product variants later can be challenging.

Advantages of Indexing Conveyors
Which Industries Use Indexing Conveyor Systems?
Indexing conveyors are widely used in industries where precision and repeatability are essential:
- Automotive and automotive components
- Electronics and PCB assembly
- Medical device and pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Packaging and consumer goods
- Precision mechanical and electromechanical assembly
Each industry demands different levels of accuracy, cleanliness, and automation integration.
How Does DNC Automation Deliver Indexing Conveyor Solutions?
DNC Automation provides custom-engineered indexing conveyor systems tailored to each production line:
- Process analysis and cycle time optimization
- Servo motion control and PLC integration
- Modular, scalable conveyor architecture
- On-site installation and commissioning
- Long-term maintenance and system upgrades
By focusing on system integration rather than standalone equipment, DNC Automation helps manufacturers achieve reliable, high-performance automation.
- 31 views
- 0 Comment

Recent Comments