Modular Conveyor Systems: Design, Flexibility, Applications & Key Considerations
Malaysian manufacturers face a reality that their European and North American counterparts encountered a decade earlier: customer demand is shifting from large uniform batches to smaller, more frequent orders of greater product variety, and the factory infrastructure must flex to match. A modu conveyor — or modular conveyor system — solves this problem with a fundamentally different design philosophy compared to conventional welded-steel belt conveyors: both the transport belt and the structural frame are built from interlocking, individually replaceable modules that can be added, removed, or reconfigured without specialist tools, welding equipment, or extended production shutdowns. The “modu” designation comes from two sources: Modu-Flex, a specific brand of aluminium profile linear transport systems by Minitec that has become a reference standard for assembly cell conveyors in Malaysian electronics manufacturing, and the broader industry use of “modu conveyor” as shorthand for any modular plastic belt conveyor built on a bolt-together aluminium frame. Both interpretations share the defining characteristic: modularity at every level, from individual belt modules that cost RM 5–20 each to replace versus RM 200–2,000 per meter of continuous rubber belt replacement. This guide covers all 6 primary modular conveyor types for Malaysian factory applications, with specifications, material selection, hygiene considerations, and financial analysis that help Malaysian manufacturers make the right modular conveyor investment.
What Is a Modu Conveyor?
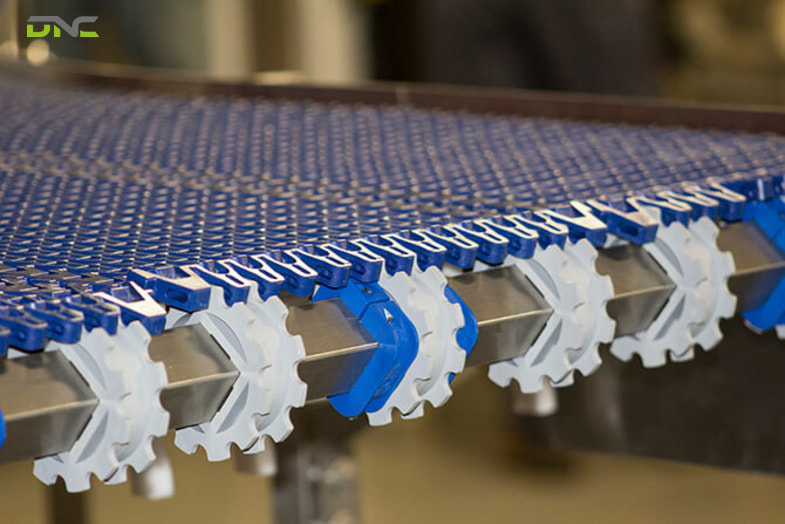
A modu conveyor is a modular conveyor system where both the belt and the structural frame are constructed from interlocking, individually replaceable components — as opposed to conventional conveyors where the belt is a continuous loop and the frame is welded steel requiring cutting and re-welding to reconfigure. Modu conveyors use interlocking plastic belt modules (manufactured from PP, POM, or PE) that hinge together on transverse rods to form a flat or structured transport surface of any required width and length. The conveyor frame is built from aluminium T-slot profile sections — 40×40 mm, 45×45 mm, or 80×80 mm cross-section — that bolt together using T-slot nuts and connection brackets from a 1,500+ item accessory catalog, enabling any conveyor geometry (straight, curved, inclined, with side rails, with workstation surfaces) to be assembled and modified without metalworking equipment. The result is a conveyor system that can be reconfigured in hours rather than days, where individual belt modules replace without removing the entire belt, and where frame sections extend or reconfigure as production layouts evolve — making modu conveyors the standard choice for Malaysian factories facing frequent product changeover, expanding production lines, and NIMP 2030 smart factory transformation.
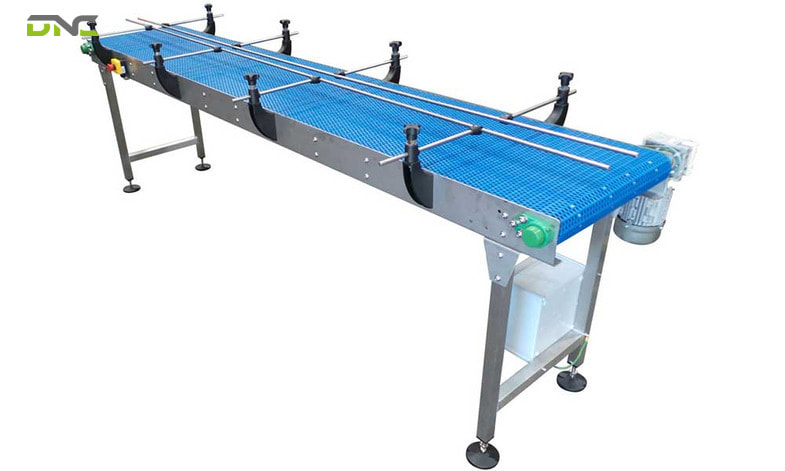

How Does a Modu Conveyor Work?
Modu conveyor operation combines the reliability of interlocking plastic belt drive with the flexibility of aluminium profile frame construction, creating a transport system that performs identically to a conventional fixed conveyor while remaining fully reconfigurable throughout its service life.
Step 1: Modular Belt Drive and Engagement
Modular plastic belts are driven by toothed drive sprockets that engage with the hinge rod sockets on the underside of each belt row. Unlike flat belt conveyors where drive friction determines the maximum torque transferable, modular belt sprocket drives are positive — each sprocket tooth positively engages a belt socket, eliminating belt slippage entirely. Drive sprockets are mounted on a drive shaft driven by a motor and gearbox through a chain or direct drive. Belt speed ranges from 0.05 m/s (precision assembly) to 2.0 m/s (high-speed F&B packaging). The positive drive engagement also prevents belt elongation — a common failure mode of rubber and PVC flat belts in high-tension drive applications.
Step 2: Belt Module Engagement and Track Support
Modular belt modules hinge at their transverse rods — each module is 25.4 mm, 38.1 mm, or 50.8 mm long in the transport direction (belt pitch) and any width from individual 25 mm wide modules to 2,500 mm wide assembled sections. The hinged construction allows the belt to wrap around drive and return sprockets, traverse radius curves (in curved conveyor configurations), and travel across conveyor frames with multiple support slider rails. Support slider rails — typically UHMWPE (ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene) — are bolted to the aluminium frame cross-members and provide the running surface for the belt modules’ underside. UHMWPE rails provide 10–15× lower friction than steel rails and last 3–5 years in continuous operation before replacement.
Step 3: Belt Return Path
Modular belts return from the tail end of the conveyor to the head end on a return rail system beneath the conveyor frame, supported by return roller or slider rail sets. Because modular belts are self-supporting (the module-to-module hinge structure maintains belt rigidity over short unsupported spans), return path support requirements are less demanding than for thin flat belts — return spans of 300–500 mm between support points are standard for modular belts versus 100–200 mm for thin flat belts.
Step 4: Frame Assembly and Reconfiguration
Aluminium T-slot profile frame sections are cut to required lengths and connected using cast aluminium angle brackets bolted into T-slot channels. No welding, grinding, or specialist metalworking is required — conveyor frame assembly uses standard socket head cap screws and a calibrated torque wrench. Adding a 500 mm conveyor extension requires: one additional aluminium profile section, two end brackets, one support cross-member, and one UHMWPE slider rail — assembly time under 30 minutes. This speed of reconfiguration is the financial differentiator for Malaysian factories with evolving production line layouts.
Step 5: PLC Control and Zone Management
Modu conveyor zones are controlled by a Siemens PLC (S7-1200 for simple single-zone systems, S7-1500 for multi-zone systems with accumulation and diverting). Speed control uses Siemens VFDs (SINAMICS G110M or G120) for zone-by-zone speed independence. For accumulation modu conveyors with zero-pressure zones, MDR (motorized drive roller) drives replace shaft drives in short accumulation zones, providing zone-level control without external drives. DNC Automation programs all modu conveyor control logic in Siemens TIA Portal, with standard function blocks for accumulation, zone control, speed coordination, and fault detection that reduce commissioning time and simplify future program modifications.
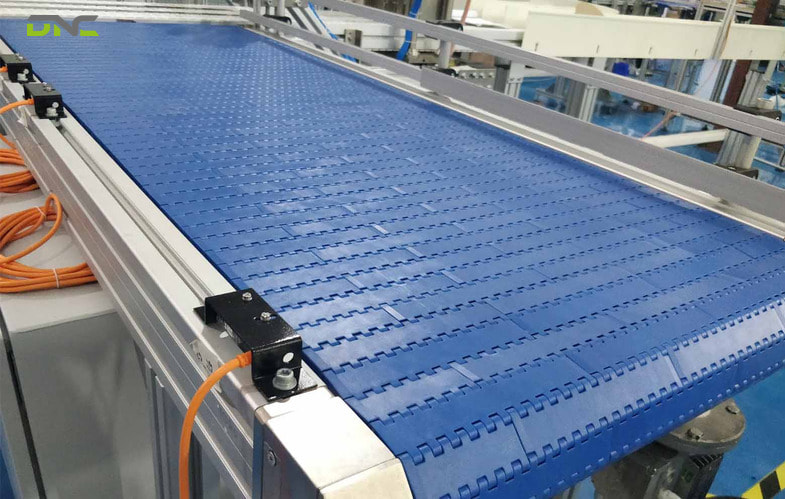

Types of Modu Conveyor
Six primary modular conveyor system types serve the full range of Malaysian manufacturing applications from F&B washdown lines to assembly cell transport.
1. Modular Flat-Top Belt Conveyor
Modular flat-top belt conveyors use closed-surface PP or POM modules that present a continuous flat carrying surface — equivalent to a flat belt conveyor in product handling performance but with the superior hygiene and maintenance characteristics of modular construction. Flat-top modular belts are the standard in Malaysian F&B and pharmaceutical manufacturing: individual module replacement without belt removal, open T-slot aluminium frame with no horizontal dead zones for bacterial accumulation, and FDA-compliant PP or POM material that tolerates cleaning temperatures to 85°C. DNC Automation specifies flat-top modular belts for all Malaysian food factory conveyor projects where daily washdown is required — eliminating the continuous belt tracking issues that plague conventional flat belts in humid Malaysian environments. F&N and Ramly Burger (DNC clients) use flat-top modular conveyors on their primary product transport lines.
2. Modular Open-Grid Belt Conveyor
Modular open-grid belt conveyors feature modules with drainage openings — typically 30–60% open area — that allow liquid, debris, and fine particles to fall through the belt surface during transport. Open-grid configurations are specified for applications requiring drainage or airflow through the belt: washing lines for fresh produce, cooling tunnels for baked goods, draining lines for blanched or steamed food products, and water-bath defrosting lines for frozen products. Open-grid modular belts maintain the same module hinge system as flat-top belts, preserving all reconfigurability and module-replacement maintenance benefits while providing drainage that flat-top or conventional rubber belts cannot deliver. Guan Chong Berhad (cocoa processing — DNC client) uses open-grid modular conveyors for cocoa bean washing and sorting operations where drainage and bean handling combine in a single transport system.
3. Modular Curve Belt Conveyor
Modular curve belt conveyors use specially designed module geometries — tapered or radius-cut modules — that allow the belt to traverse a radius turn without a separate transfer unit. Radius turns from 90° to 180° with turning radii from 150 mm to 2,000 mm enable conveyor layouts that navigate corners within the factory floor plan without product transfer points. Transfer-free curves reduce product drop height (product does not fall between conveyors at a transfer), preventing product damage and reducing line noise. Modular curve conveyors are specified in Malaysian F&B factories where floor space constraints require conveyor routing around structural columns, through doorways, or along irregular building perimeters. The DNC Automation standard curved conveyor design uses Minitec Modu-Flex curve sections with ±1° angular adjustment that accommodates minor installation alignment errors without belt stress.
4. Modular Incline Belt Conveyor
Modular incline conveyors use cleated or textured module surfaces to transport products up steep inclines — 20°–45° — that flat-top modules cannot achieve without product slip. Cleated modular belts feature factory-moulded plastic cleats (10–50 mm height) at regular pitch intervals on standard modular belt rows, eliminating the adhesive bond failure risk of add-on cleats on flat belts. Textured module surfaces (raised diamond or dot pattern) increase friction for inclines to 25° without cleats. Modular incline belts are used in Malaysian food factories for: elevation of biscuit and snack products from baking to packaging height, transport of fresh produce from ground-level reception to elevated sorting platforms, and inclined transport of bagged or boxed products to mezzanine storage levels.
5. Washdown Modular Conveyor
Washdown modular conveyors combine stainless steel SS304 or SS316 aluminium-free frames with FDA-compliant modular belts (PP, POM, or PE) and IP69K-rated drives (drum motors fully enclosed) to create conveyor systems capable of full CIP (clean-in-place) or COP (clean-out-of-place) cleaning procedures. Full CIP involves circulating hot water (80–85°C) and cleaning solutions through the conveyor while it runs — sanitizing all product-contact surfaces without disassembly. COP involves removing the modular belt for external cleaning in a dedicated washing station. Washdown modular conveyors are mandatory in Malaysian high-care food zones: ready-to-eat meat processing, fresh seafood processing, and pharmaceutical tablet and capsule manufacturing. DNC Automation designs washdown modular conveyors with sloped drip trays, centralized drainage, spray bar positions, and documented cleaning validation protocols that satisfy HACCP MS 1480 critical control point requirements.
6. Modu-Flex / Aluminium Profile Modular Transport
Modu-Flex systems by Minitec — and equivalent systems from FlexLink (Sweden), Bosch Rexroth, and mk Technology Group — represent the assembly cell standard for modular transport in Malaysian electronics, automotive component, and precision manufacturing. Modu-Flex systems use the 45×45 mm aluminium T-slot profile as the universal frame element, combining it with a modular flat-top or cleated belt transport section. The result is an assembly workstation that integrates belt transport, work surface, overhead tool rails, sensor mounting, and guarding from a single T-slot accessory catalog — enabling complete assembly cell layout changes in 4–8 hours versus 2–5 days for equivalent welded steel reconfiguration. Malaysian EMS factories in Penang use Modu-Flex for post-SMT assembly cell transport, where board product mix changes require rapid conveyor width and height adjustment between product runs.
Modu Conveyor Type Comparison Table
| Type | Belt Material | Open Area | Incline | Washdown | Best Application |
| Flat-Top | PP/POM/PE | 0% | 0°–15° | Yes (IP65+) | F&B, pharma, packaging |
| Open-Grid | PP/POM/PE | 30–60% | 0°–15° | Yes | Washing, cooling, draining lines |
| Curve | PP/POM | 0% | 0°–10° | Yes | Layout corner turns |
| Incline Cleated | PP/POM | 0% | 20°–45° | Yes | Elevation, bulk loose products |
| Washdown | PP/POM/PE | 0–30% | 0°–20° | Full CIP/COP | High-care food, pharma |
| Modu-Flex Assembly | PP/POM | 0% | 0°–5° | Moderate | Electronics, precision assembly |
Key Components of a Modu Conveyor System
A complete modu conveyor system integrates the modular belt, aluminium profile frame, drive system, and control architecture into a cohesive transport cell that delivers both operational performance and long-term reconfigurability.
Modular Belt Modules. PP (polypropylene) modules are the standard choice — FDA-compliant, operating temperature -30°C to +110°C, resistant to most food acids and bases, lower cost than POM. POM (polyoxymethylene / acetal) modules offer higher stiffness and lower friction than PP — specified for higher speed applications (above 1.0 m/s) and for applications where module deflection under load must be minimized. PE (polyethylene) modules provide the highest chemical resistance and lowest friction coefficient — specified for extremely aggressive chemical environments and lubricated (wet) conveyor applications. Module colors: white (food standard), blue (visual contamination detection — preferred for food by many HACCP auditors), natural (standard industrial), black (UV-stable outdoor applications).
Hinge Rods. Stainless steel SS316 hinge rods connect adjacent belt module rows at each belt pitch. SS316 hinge rods resist corrosion in aggressive food environments where SS304 rods may pit within 12 months of chlorine-based cleaning chemical exposure. DNC Automation specifies SS316 hinge rods as standard for all Malaysian food processing environments.
Aluminium Profile Frame. 45×45 mm T-slot aluminium profile (anodized) provides the universal frame element. Profile cross-section designation: Item 8 45×45 (Item Germany standard) or Minitec equivalent. Anodized finish provides surface hardness of 350–500 HV (versus 60–80 HV for bare aluminium), resisting abrasion from conveyor accessories and providing corrosion resistance in 95% RH tropical Malaysian environments for 10+ years without paint degradation.
UHMWPE Slider Rails. Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene slider rails, bolted to frame cross-members, provide the low-friction running surface for the modular belt. UHMWPE has a coefficient of friction of 0.10–0.15 against PP belt modules (versus 0.20–0.35 for steel) and a wear life of 3–5 years in continuous operation. UHMWPE is FDA-compliant and resistant to all common food processing chemicals.
Drive Motor and Gearbox. SEW-Eurodrive or Bonfiglioli geared motors (0.09–1.1 kW for standard modular conveyors) with Siemens SINAMICS VFD for speed control. Drum motor drives — where the motor and gearbox are enclosed inside the drive drum — provide the highest hygiene rating for food-zone drives and eliminate the external gearbox that accumulates food residue on conventional drive configurations.
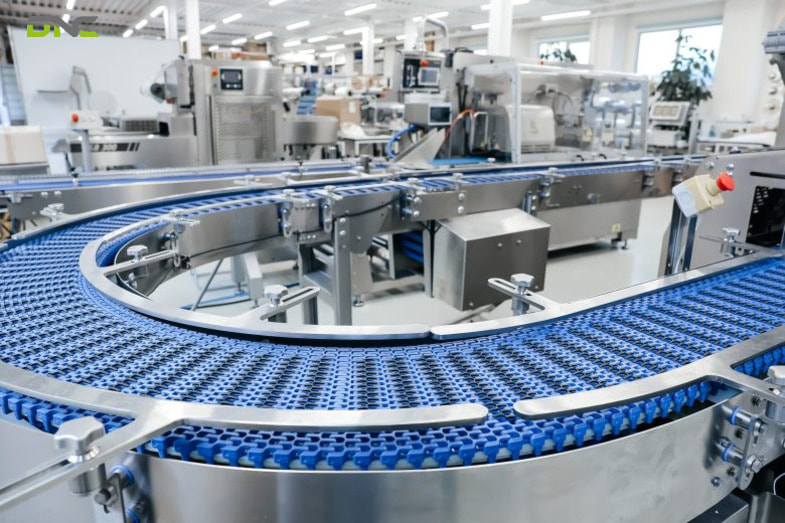

Applications: Where Modu Conveyors Are Used in Malaysian Manufacturing
Modu conveyors serve Malaysian manufacturing sectors where conventional fixed conveyors create inflexibility costs — production line changes, hygiene demands, and growth expansion requirements.
F&B Manufacturing — Selangor and Johor
Malaysian food manufacturers face a combination of hygiene requirements and product mix variability that makes modular conveyors the optimal transport solution. Tropical humidity accelerates rubber and PVC belt degradation — conventional flat belts in F&B environments achieve 12–18 months service life before cracking, delamination, or contamination risk forces replacement. Modular PP or POM belts last 3–5× longer in equivalent environments, reducing belt replacement frequency and the associated production stoppages. DNC Automation client Ramly Burger operates modular flat-top conveyor lines for halal beef patty transport, where HACCP-required daily washdown cleaning is performed using hot water (75°C) and alkaline detergent — a cleaning regime that PP modular belts tolerate indefinitely, while PVC flat belts would fail within 6 months of exposure. Guan Chong Berhad uses open-grid modular conveyors for cocoa processing, where nibs require drainage during transport.
Penang Electronics Manufacturing
Penang EMS factories — Benchmark, ESCATEC, Flex, and QDOS — use Modu-Flex aluminium profile assembly conveyors as the standard infrastructure for post-SMT assembly cell transport. EMS factories change board product mix every 2–4 weeks, requiring conveyor width adjustment (PCB widths range from 100 mm to 450 mm), height adjustment for operator ergonomics, and side rail reconfiguration for different PCB thickness and fixture heights. Modu-Flex systems accommodate these changes in under 4 hours without workshop tools or specialist engineers. DNC Automation’s Penang branch supplies and installs Modu-Flex systems with Siemens S7-1200 PLC speed control and IO-Link sensor connectivity, providing EMS factories with the operational flexibility that NIMP 2030 high-mix manufacturing demands.
Pharmaceutical and Medical Device — Selangor
Hartalega (glove manufacturing — DNC client) and pharmaceutical manufacturers in the Selangor industrial corridor use washdown modular conveyors for glove stripping, powder donning, and quality inspection transport. Full CIP capability is required in glove manufacturing for cleaning of residual powder, polymer compounds, and chemical residues from conveyor belt surfaces. Modular belt individual module replacement allows a single contaminated module to be removed and replaced in under 2 minutes without stopping the entire belt — a maintenance advantage over continuous belts that require full belt removal and replacement when contamination is detected in one section.
Benefits of Modu Conveyor Systems for Malaysian Factory Operations
Modular conveyor systems deliver financial and operational benefits across three dimensions: maintenance cost, production flexibility, and hygiene compliance — all critical for Malaysian manufacturers operating under NIMP 2030 transformation pressure.
Belt maintenance cost reduction of 40–60%. Individual modular belt module replacement costs RM 5–20 per module. A typical conveyor belt failure (cracking, delamination, contamination) on a continuous flat belt requires replacing the entire belt: RM 200–2,000/m for a 2–3 mm food-grade PU belt. On a 10-meter modular conveyor, a localized belt damage event requiring 10 module replacements costs RM 50–200 versus RM 2,000–20,000 for a full belt replacement on a conventional conveyor. Over a 5-year period, this difference represents RM 30,000–RM 200,000 in reduced belt maintenance costs for a single conveyor line.
Reconfiguration in hours, not days. Malaysian manufacturers implementing NIMP 2030 smart factory transformations are adding automation cells, robotic integration, and new product lines on timelines of months rather than years. Conventional welded steel conveyor modifications require metalworking trades, hot work permits, and production area shutdowns of 2–5 days. Modular aluminium profile conveyor reconfigurations require only standard tools, no hot work permits, and production shutdown times of 4–24 hours. For a factory running two shifts at RM 5,000/hour production value, saving 24 hours of shutdown time represents RM 240,000 in preserved production value per reconfiguration event.
Hygiene compliance for HACCP and halal certification. Aluminium T-slot frame construction eliminates the horizontal flat surfaces and internal hollow sections of conventional welded steel frames where water and food residue accumulate — a critical HACCP compliance advantage. Modular belt individual module replacement eliminates the risk of accumulating contamination at belt cracks or delamination points that form in conventional flat belts after extended use. DNC Automation’s modular conveyor installations consistently satisfy SIRIM HACCP and JAKIM halal certification audits on first assessment, versus conventional conveyor installations that frequently require modification to meet auditor hygiene requirements.
SAG Grant eligibility for modular conveyor investment. Malaysia’s Smart Automation Grant (SAG) funds automation investments that measurably improve productivity and reduce labor dependency. Modular conveyor systems that replace manual cart transport or fixed conveyor systems with flexible automated transport — documented with baseline and post-installation productivity measurement — qualify for SAG funding of up to RM 700,000 (70% of RM 1,000,000 maximum, 70:30 matching). DNC Automation has assisted multiple Malaysian food and electronics manufacturers in securing SAG funding for modular conveyor automation projects, with average grant amounts of RM 350,000–RM 600,000 per project.
How to Choose the Right Modu Conveyor for Your Factory
Selecting the optimal modu conveyor configuration for a Malaysian manufacturing application requires evaluating five parameters that determine both the belt type and frame specification.
Product contact requirement. Direct food contact requires FDA-compliant PP or POM modules in white or blue (contamination visibility), SS316 hinge rods, and SS304 or SS316 frame construction. Indirect food contact (packaged products) permits standard PP modules with anodized aluminium frame. Non-food applications (electronics, automotive components) can use standard PP or POM modules with standard anodized aluminium frame.
Cleaning protocol intensity. Full CIP (circulating hot water, 80–85°C, cleaning chemicals): specify POM modules (PP may deform at sustained temperatures above 80°C), SS316 hinge rods, IP69K drum motor drives, and sloped drip tray frames. Daily washdown (hose-down, 60–70°C): PP modules with SS304 hinge rods, IP65 drive, anodized aluminium frame. Periodic cleaning (weekly or less): standard PP modules, standard anodized frame, IP54 drive.
Production change frequency. If conveyor layout changes occur more than once per year: specify full aluminium T-slot profile frame with standard bolt-together accessories — reconfiguration cost is recovered within 2 layout changes. If layout is fixed for 5+ years: stainless steel fixed frame may be more cost-effective than aluminium profile for food applications.
Product size range and incline requirement. Wide products (above 600 mm): specify modular flat-top belt up to 2,500 mm width in modular construction. Steep incline (above 20°): specify cleated modular belt. Radius turns required: specify modular curve belt sections. Drainage required: specify open-grid modules.
Consult DNC Automation for complete modu conveyor specification. DNC Automation’s 35+ engineers design, supply, and install complete modu conveyor systems for Malaysian manufacturing — from single-section assembly workstation conveyors to 50-station modular production lines with Siemens PLC automation, vision inspection, and MES data connectivity. Get a Free Consultation to evaluate the financial and operational benefits of modular conveyor conversion for your Malaysian factory.
Frequently Asked Questions About Modu Conveyors
What is the difference between a modu conveyor and a conventional flat belt conveyor?
A modu conveyor uses interlocking plastic modules (PP, POM, or PE) as the belt and an aluminium T-slot profile as the frame — both components are individually replaceable without specialist tools. A conventional flat belt conveyor uses a continuous PVC, PU, or rubber belt that must be removed entirely for replacement, mounted on a welded steel frame that requires metalworking to reconfigure. Key differences: modu conveyor belt replacement cost is RM 5–20/module versus RM 200–2,000/m for flat belt; modu conveyor frame reconfiguration takes hours versus days for welded steel; modu conveyor hygienic design better satisfies HACCP MS 1480 requirements. The trade-off: modular conveyors cost 20–40% more than equivalent flat belt conveyors in initial capital cost, with the cost difference recovered in 12–24 months through belt maintenance savings and reconfiguration time savings.
Are modu conveyor belts food-grade certified?
PP and POM modular belt modules are available with FDA 21 CFR 177 certification and EU Regulation 10/2011 compliance from major belt manufacturers including Intralox, Rexnord, and Habasit. DNC Automation supplies only certified food-grade modules for all Malaysian food factory installations, with full material compliance documentation provided as part of the project handover package. Module color white or blue is preferred for food applications — white for general food contact, blue for high-visibility contamination detection in ready-to-eat zones.
Can a modu conveyor handle curves and elevation changes?
Modular belt conveyors handle elevation changes (inclines) using cleated module surfaces rated for slopes to 45°. Radius turns from 90° to 180° are handled using purpose-designed radius belt modules or by using standard belt sections on radius roller curves. Modu-Flex aluminium profile systems accommodate 3D conveyor geometries — multiple elevation changes and corner turns within a single assembly cell — using the 1,500+ item T-slot accessory catalog that includes angled connectors, height-adjustable legs, and corner joining plates.
How does tropical humidity in Malaysia affect modu conveyor performance?
Malaysian tropical humidity (80–95% RH year-round) has minimal impact on properly specified modular conveyors. PP and POM belt modules are inherently hydrophobic — they do not absorb moisture, swell, or degrade in humid environments. Anodized aluminium frames are corrosion-resistant at tropical humidity levels for 10+ years. SS316 hinge rods resist corrosion in food environments with chlorine-based cleaning chemicals. The primary humidity-related maintenance requirement is inspection of drive motor bearing seals — DNC Automation specifies IP65 minimum drives for all Malaysian modular conveyor installations, with IP69K for high-humidity or washdown environments. Conventional rubber and PVC flat belts, by contrast, degrade 40–60% faster in Malaysian tropical humidity than in temperate European environments, making modular plastic belts a materially superior choice for Malaysian factory conditions.
What is the maximum width and speed of a modu conveyor?
Standard modular belt maximum width: 2,500 mm (achieved by assembling modules side-by-side across the belt width). Maximum practical belt speed for standard modular conveyors: 2.0 m/s (limited by modular belt noise and vibration at higher speeds). For applications requiring higher speed, conventional flat belt conveyors (to 5 m/s) or linear motor systems (to 4 m/s) are specified instead of modular belts. Modular belt width flexibility is a key advantage — changing from a 400 mm wide product to an 800 mm wide product requires adding modular sections across the belt width rather than replacing the entire belt and potentially the frame, as would be required with a conventional flat belt conveyor.
How does NIMP 2030 affect the demand for modu conveyor systems in Malaysia?
NIMP 2030’s target of converting 3,000 Malaysian factories to smart factory status by 2030 directly increases demand for modu conveyor systems in two ways. First, smart factory conversion requires automated flexible material flow — modu conveyors provide the platform flexibility that allows automated conveyor layouts to evolve as production lines add robots, vision systems, and automated storage without requiring complete conveyor replacement. Second, NIMP 2030 supports the SAG Grant (RM 1 million, 70:30 MIDA matching) for automation investments that include flexible modular conveyor systems. DNC Automation is Malaysia’s #1 factory automation company for NIMP 2030-aligned investments — our engineers design modular conveyor systems that satisfy both the technical requirements of smart factory automation and the documentation requirements of SAG Grant applications.
Conclusion
Modu conveyors — whether interpreted as Modu-Flex aluminium profile assembly transport or modular plastic belt conveyor systems — represent the correct infrastructure investment for Malaysian manufacturers facing high-mix production, hygiene compliance requirements, and NIMP 2030 smart factory transformation. The financial case is clear: 40–60% lower belt maintenance cost, reconfiguration in hours rather than days, and superior HACCP MS 1480 hygienic design that supports food safety and halal certification. DNC Automation designs, supplies, and installs complete modu conveyor systems for Malaysia’s leading food, electronics, and pharmaceutical manufacturers — including F&N, Ramly Burger, Guan Chong Berhad, and Hartalega — with Siemens PLC automation, full compliance documentation, and 24/7 local support. Talk to Our Engineers for a Free Consultation on modular conveyor systems for your Malaysian factory. Explore our related guide on [Green Conveyor Belts](/blog/green-conveyor-belt) for food-grade belt material selection detail.
- 23 views
- 0 Comment


Recent Comments