Cleated Conveyor Belt Explained: Types, Materials, Applications, and Design Considerations
Cleated conveyor belts are widely used in material handling systems where product stability, inclined conveying, and controlled material flow are required. By using raised cleats on the belt surface, they help prevent material rollback, reduce spillage, and maintain consistent positioning in automated production environments.
This article explains how cleated conveyor belts work, the most common cleat designs and materials, and where they are typically applied in industrial automation systems.
What Is a Cleated Conveyor Belt and How Does It Function in Industrial Conveyor Systems?
A cleated conveyor belt is an engineered conveyor belt solution designed to transport materials in situations where gravity, inclination, or unstable product geometry would compromise movement on a flat belt.
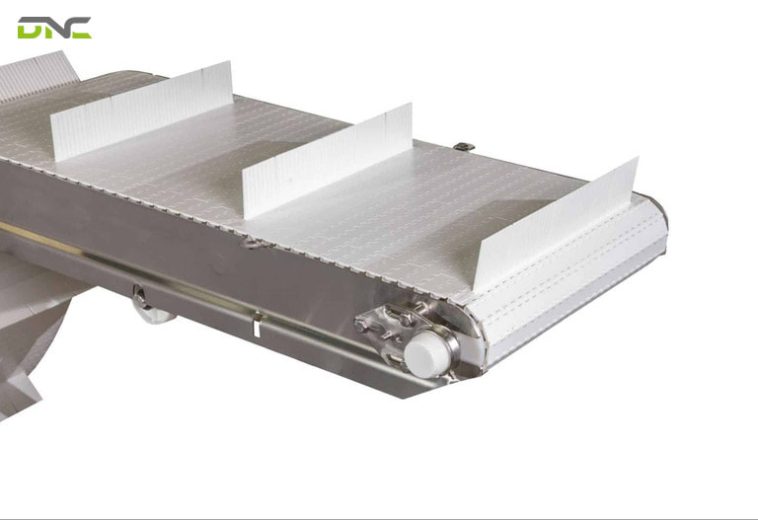
Unlike conventional flat conveyor belts, cleated conveyor belts incorporate raised profiles—referred to as cleats—mechanically bonded or molded onto the belt surface. These cleats divide the belt into defined carrying zones, enabling controlled material movement across horizontal, inclined, and even near-vertical paths.
From an engineering standpoint, cleated conveyor belts function as a hybrid between continuous conveying and segmented material control, bridging the gap between simple belt conveyors and more complex vertical handling systems.
Why Are Cleated Conveyor Belts Essential in Modern Material Handling Applications?
Cleated conveyor belts are not simply optional accessories; they are often a functional requirement in automated material handling.
They become essential when:
- Material must be conveyed upward or downward without rollback
- Product positioning must remain consistent for automation
- Bulk or irregular materials must be contained during transport
In high-throughput factories, even minor material slippage can cascade into misfeeds, machine stoppages, or quality defects. Cleated conveyor belts mitigate these risks by enforcing mechanical control rather than relying solely on friction.
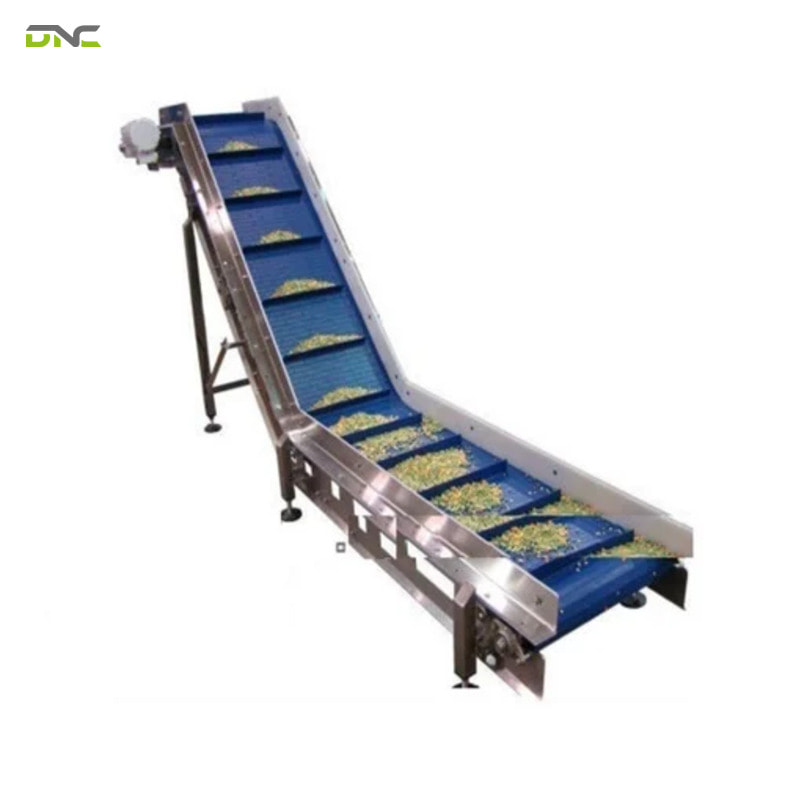

Cleated conveyor belts are not simply optional accessories; they are often a functional requirement in automated material handling.
What Types of Cleats Are Used on Cleated Conveyor Belts?
Cleats are the functional elements that distinguish cleated conveyor belts from flat belts. Their shape, height, spacing, and rigidity determine how materials are supported, restrained, and guided during transport.
How Do Straight Cleats Support Simple Separation and Inclined Conveying?
Straight cleats are linear profiles mounted perpendicular to the belt’s direction of travel. They divide the belt surface into uniform segments, each acting as a discrete carrying zone.
Functional behavior:
- Prevent backward sliding of products on moderate inclines
- Maintain consistent spacing between items
Provide predictable and repeatable material positioning
Best-suited applications:
- Uniform, rigid, or packaged products
- Cartons, boxes, and containers
- Low to medium incline angles
Technical trade-offs: Straight cleats offer excellent belt flexibility and low mechanical stress, but they provide minimal lateral containment. As a result, they are less effective for loose or irregular materials that tend to shift sideways.
Why Do T-Cleats Provide Superior Holding Capacity on Steep Inclines?
T-cleats feature an extended top flange that increases the contact surface between the cleat and the material being conveyed.
Functional behavior:
- Create a stronger mechanical stop against gravity
- Support heavier loads without rollback
- Enable steeper incline angles than straight cleats
Best-suited applications:
- Heavy bulk materials
- Dense or high-mass products
- Steep or high-elevation conveyors
Technical trade-offs: The increased cleat mass and height result in higher bending stress as the belt passes over pulleys. This requires larger pulley diameters and stronger bonding methods to ensure long-term durability.
How Do V-Cleats Improve Material Guidance and Reduce Side Spillage?
V-cleats are arranged in an angled or chevron pattern that directs materials toward the center of the belt.
Functional behavior:
- Automatically center materials during transport
- Reduce lateral drift on wide belts
- Minimize material loss at belt edges
Best-suited applications:
- Granular or free-flowing materials
- Agricultural products and recyclables
- Applications requiring moderate incline conveying
Technical trade-offs: While V-cleats enhance material guidance, they introduce additional shear forces on the belt surface. They are most effective for flow control rather than extreme incline retention.
Why Are Corrugated Cleats Used in Dynamic or High-Stress Applications?
Corrugated cleats incorporate a flexible or wavy profile that allows them to bend and deform without cracking.
Functional behavior:
- Absorb impact from dropped or uneven materials
- Reduce stress concentration at the cleat base
- Maintain performance under frequent start-stop cycles
Best-suited applications:
- High-speed conveyors
- Systems with small pulley diameters
- Environments with shock loading
Technical trade-offs: Corrugated cleats generally provide lower holding capacity than rigid cleats but significantly improve durability and belt life in demanding operational conditions.

Cleats are the functional elements that distinguish cleated conveyor belts from flat belts.
How Are Cleated Conveyor Belts Classified by Material?
Cleated conveyor belts are classified by material based on how the belt compound performs under mechanical stress, environmental exposure, and interaction with the conveyed product. Material selection directly affects cleat adhesion strength, belt flexibility, wear resistance, hygiene compliance, and long-term system reliability.
Cleated conveyor belts are commonly grouped into the following material categories:
- PVC cleated conveyor belts: PVC belts are widely used in light to medium-duty applications where operating conditions are relatively stable. They offer good flexibility, making them suitable for systems with smaller pulley diameters.
- PU cleated conveyor belts: PU belts are engineered for applications requiring high hygiene standards and resistance to oils, fats, and abrasion. Their smooth, non-porous surface supports frequent cleaning and washdown procedures without compromising cleat bonding.
- Rubber cleated conveyor belts: Rubber belts are designed for heavy-duty applications involving high impact, abrasive materials, or uneven loading. They provide excellent tensile strength, shock absorption, and resistance to tearing.
- Specialty material cleated conveyor belts: Specialty belts are developed to meet specific operational challenges that standard materials cannot handle.
The choice of belt material has a direct impact on service life, maintenance frequency, energy efficiency, and overall conveyor system stability. Selecting the appropriate material ensures that cleated conveyor belts perform reliably as integrated components of automated material handling systems.
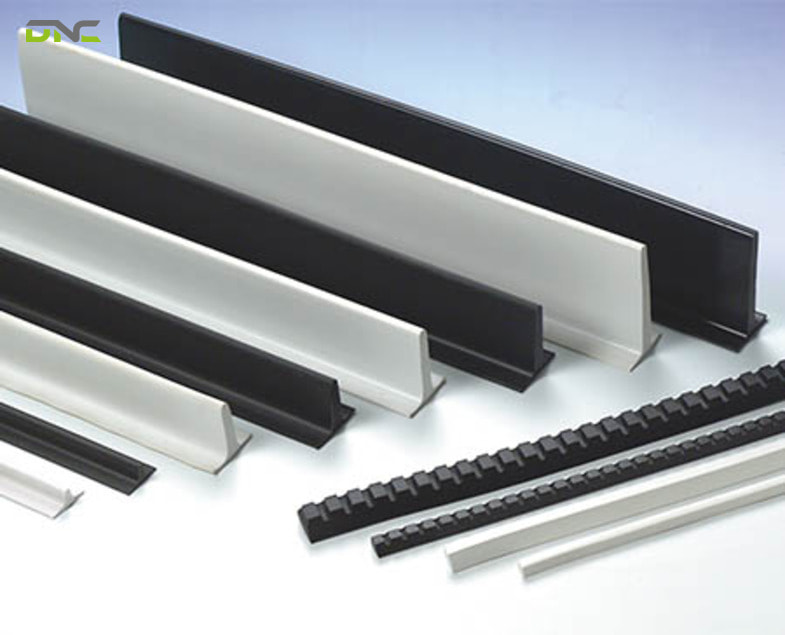

Material selection directly affects cleat adhesion strength, belt flexibility, wear resistance, hygiene compliance, and long-term system reliability.
Which Industries Commonly Use Cleated Conveyor Belts?
Cleated conveyor belts are commonly used in industries that require stable material transport, especially on inclined conveyors or in automated systems.
Typical industries include:
- Food and beverage processing: Used to move products on inclines while maintaining spacing and product position throughout the production line.
- Agriculture and bulk handling: Help transport loose materials such as grains and crops without rollback or spillage.
- Logistics and warehousing: Maintain package stability during elevation changes in automated sorting and distribution systems.
- Packaging and manufacturing: Ensure consistent feeding of products into automated machines and reduce misfeeds.
- Recycling and waste processing: Handle irregular and heavy materials with improved containment and reduced material loss.
Across these industries, cleated conveyor belts support reliable material flow and consistent throughput in automated operations.
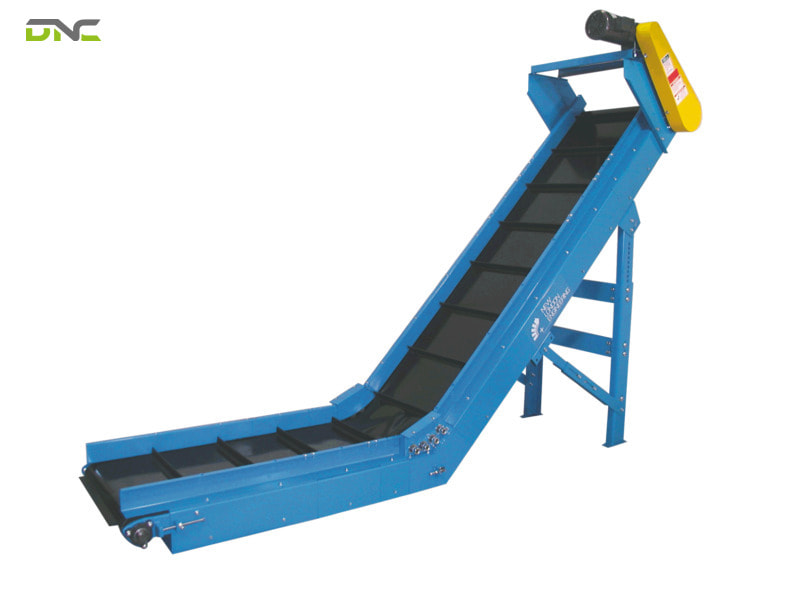

Cleated conveyor belts are commonly used in industries that require stable material transport
Why Choose DNC Automation for Cleated Conveyor Belt System Design?
DNC Automation is selected not for individual components, but for its system-level approach to cleated conveyor belt design within automated material handling environments.
Key reasons include:
- System-first engineering mindset: Cleated conveyor belts are designed as part of the complete conveyor and automation system, ensuring compatibility with structure, drives, and control logic.
- Application-driven design approach: Belt geometry, cleat configuration, and material selection are determined based on actual material behavior and process requirements, not generic standards.
- Experience across diverse industrial environments: Designs reflect real-world challenges such as inclined conveying, bulk material handling, and high-throughput operations.
- Focus on long-term reliability: Emphasis is placed on durability, maintainability, and stable performance throughout the system lifecycle.
- Automation-oriented thinking: Every cleated conveyor belt solution is evaluated by its impact on upstream and downstream automation processes.
This approach allows DNC Automation to deliver cleated conveyor belt systems that perform reliably under real production conditions.
- 28 views
- 0 Comment



Recent Comments