IoT in Warehouse Management: Smart Solutions for Your Warehouse
The Internet of Things (IoT) in a warehouse refers to a network of physical objects—assets, equipment, inventory, and environment equipped with sensors, software, and connectivity to collect and exchange data in real-time. This network transforms a traditional facility into a smart warehouse in Malaysia by enabling machine-to-machine (M2M) interaction and creating a connected logistics ecosystem. This raw data is often sent to a central platform like a Warehouse Management System (WMS) or a cloud computing environment for processing.
How IoT Enhances Visibility and Control?
IoT devices provide real-time monitoring and tracking of every aspect of the warehouse, from the location and condition of a specific pallet to the operational status of a conveyor belt. This eliminates manual checks and provides high-level visibility, which is the cornerstone of warehouse digitalization.
- Real-Time Tracking: Sensors (e.g., RFID) track inventory and assets, providing instant location and status updates.
- Data-Driven Warehouse: The data is analyzed to create IoT dashboards and reports, allowing managers to make fast, informed, and data-driven warehouse decisions, offsetting potential supply chain disruptions.
How IoT Enhances Visibility and Control?
What are the components of an IoT-Enabled Warehouse?
The core components that enable this transformation include:
| Component | Function | Technology |
| Smart Sensors | Collect data on location, temperature, humidity, vibration, etc. | RFID, Bluetooth beacons, GPS, AI cameras |
| Data Gateways | Aggregate data from sensors and connect them to the network. | IoT Gateways |
| Edge Computing | Processes data locally near the source to reduce latency and bandwidth usage. | Local servers/devices |
| Software | Stores, manages, and analyzes the data for actionable insights. | WMS, cloud platforms, data analytics tools |
What are the Applications of IoT in a Warehouse?
Asset and Inventory Tracking
IoT is crucial for achieving high inventory accuracy. Using technologies like RFID tracking Malaysia and smart shelves, businesses can automatically monitor stock levels, location, and movement of goods (raw, WIP, or finished), preventing stockouts, overstocking, and minimizing human errors in inventory counting.
Predictive Maintenance for Equipment
Downtime from equipment failure is costly. Predictive maintenance IoT uses sensors attached to machinery (forklifts, conveyors, ASRS) to continuously monitor their condition. By analyzing vibrations, temperature, and performance data, the system can detect signs of wear and tear, alerting maintenance teams to potential issues before they lead to a breakdown. This minimizes unplanned downtime and extends equipment lifespan.
Environmental and Energy Monitoring
IoT sensors monitor critical environmental conditions like temperature and humidity (HVAC monitoring IoT) to ensure goods (especially perishables or pharmaceuticals) are stored in optimal conditions. Additionally, smart sensors can manage energy consumption, for instance, by implementing smart lighting warehouse systems that adjust based on occupancy, supporting the move toward an energy-efficient warehouse.
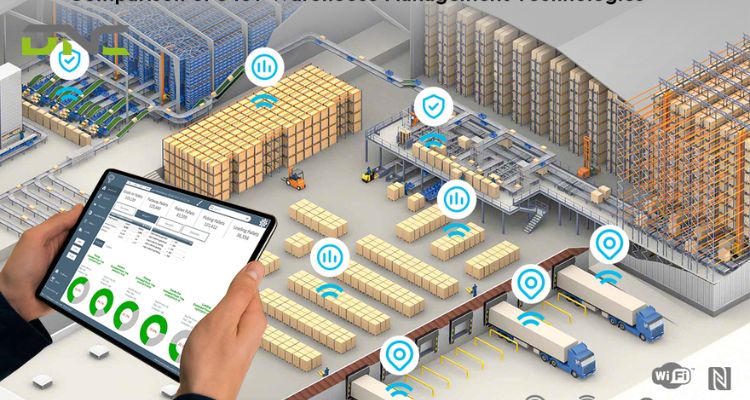

What are the Applications of IoT in a Warehouse?
How Does IoT Integrate with ASRS, AGVs, and Conveyor Systems?
IoT acts as the nervous system for advanced automation. It provides the real-time communication and data necessary for:
- ASRS IoT Integration: Communicating inventory locations and retrieval requests to Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS) for efficient operation.
- AGV IoT Communication: Guiding Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) using geolocation and path optimization data to prevent collisions and streamline material flow.
- Conveyor Sensors: Monitoring the health and throughput of conveyor systems for seamless operations.
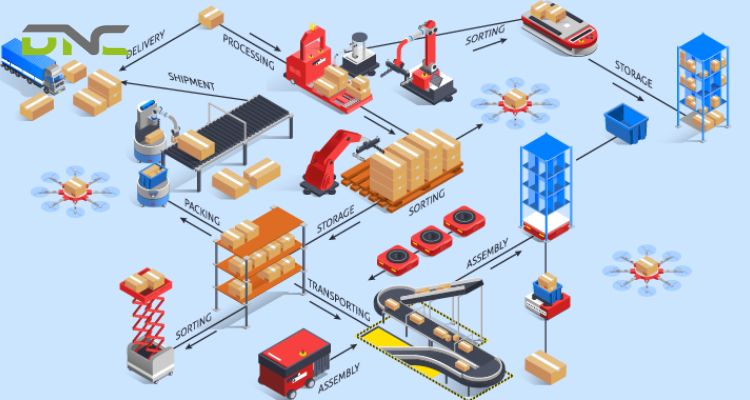
How Does IoT Integrate with ASRS, AGVs, and Conveyor Systems?
What are the Benefits of Implementing IoT?
Improved Efficiency and Reduced Operational Costs
By eliminating manual processes, minimizing errors, and optimizing workflows, IoT dramatically improves operational efficiency. Process automation efficiency in tasks like picking and packing leads to faster cycle times and order fulfillment. Over time, this results in significant IoT ROI through labor cost savings, reduced waste, and maximized use of existing space.
Enhanced Safety and Compliance
IoT devices, such as safety sensors and wearables, can monitor the warehouse environment and worker well-being. This allows for workplace safety IoT solutions that can detect unauthorized access, monitor environmental hazards, and implement accident prevention sensors to reduce the risk of injuries, ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
Better Decision-Making with Data Analytics
The constant stream of data from IoT sensors feeds into powerful IoT analytics dashboards. This data allows managers to track key performance indicators (KPIs) in real-time, gain valuable insights into usage patterns, and perform root-cause analysis on bottlenecks, transforming the warehouse into a truly data-driven warehouse.

What are the Benefits of Implementing IoT?
Which Challenges Are Adopting IoT in Warehousing?
Adopting IoT in warehouses isn’t always easy. Many businesses face hurdles like cybersecurity risks, outdated systems, and the need for new digital skills. Overcoming these challenges is key to building truly smart and connected warehouses.
- Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Concerns: As warehouses become interconnected, they become more vulnerable to cyber threats. IoT warehouse security is paramount. Implementing strong authentication, encryption, and robust data protection protocols is essential to safeguard sensitive inventory and operational data from unauthorized access or network attacks.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: A common barrier is the challenge of IoT integration challenges with outdated, existing infrastructure. Many companies run on legacy system modernization which can be complex and costly. A phased approach or selecting solutions with flexible integration capabilities (like open APIs) is crucial for a smooth WMS upgrade.
- Workforce Training and Change Management: The transition to a smart warehouse requires a digitally-skilled workforce. The adoption of new technology necessitates investment in warehouse automation training and workforce upskilling to ensure employees have the digital skills Malaysia needs to operate and maintain the new IoT and automation systems.
Conclusion
Embracing IoT in warehouse management is no longer just an innovation — it’s a necessity for businesses seeking to remain competitive in today’s rapidly evolving logistics landscape. From real-time tracking to predictive maintenance, IoT brings visibility, efficiency, and intelligence to every corner of warehouse operations.
At DNC Automation, we specialize in helping businesses integrate smart IoT solutions tailored to their unique needs, from ASRS and AGVs to conveyor systems and WMS integration. Partner with us today to transform your warehouse into a connected, data-driven environment ready for Industry 4.0.
- 47 views
- 0 Comment

Recent Comments